What is Calibration?
Calibration is the process of adjusting and verifying the accuracy and precision of a measuring instrument or tool by comparing its measurements to known standards. This is done to ensure that the instrument provides accurate and reliable measurements, as well as to detect and correct any deviations or errors that may have occurred. Calibration is typically performed using specialized equipment and procedures, and it may involve adjusting various parameters or settings on the instrument, such as its sensitivity, zero point, or linearity. Calibration is important in a wide range of industries and applications, including manufacturing, laboratory testing, environmental monitoring, and medical diagnostics, among others.

What is a Magnetic Flow Meter?
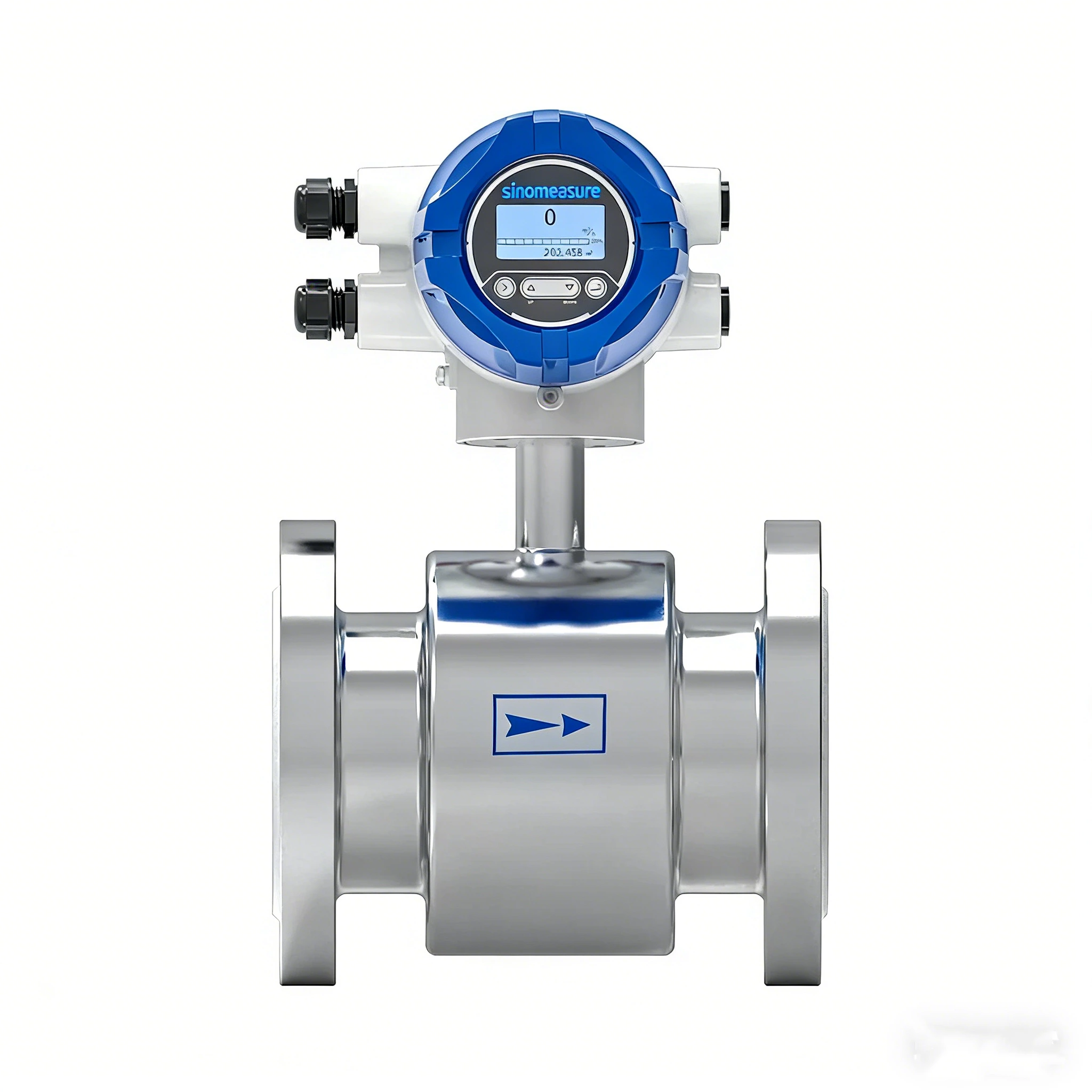
A magnetic flow meter, also known as a magmeter, is a type of flow meter that measures the flow rate of conductive liquids. It works by utilizing Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, which states that a voltage is induced in a conductor as it moves through a magnetic field. In a magmeter, the conductive liquid acts as the conductor, and two coils located outside the pipe create a magnetic field. As the liquid flows through the pipe, it generates a voltage that is proportional to the flow rate, which is then measured by the meter.
Magmeters are popular in industries such as water and wastewater, chemical processing, and food and beverage, due to their high accuracy, low maintenance, and ability to measure a wide range of flow rates. They are especially useful for measuring dirty or abrasive liquids, as they have no moving parts that can become clogged or damaged. Additionally, magmeters can be used to measure flow in both directions, making them a versatile option for various applications.
What is Flow meter Calibration?
Flow meter calibration is the process of determining the accuracy and reliability of a flow meter. This is done by comparing the flow meter's measurement of a known quantity of fluid with the actual quantity of fluid that has been passed through the meter. The purpose of flow meter calibration is to ensure that the flow meter is operating correctly and accurately, as even minor errors in measurement can have significant consequences in many industries, such as oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment. Calibration is typically carried out by a trained technician using specialized equipment, and the frequency of calibration depends on the specific application and industry standards.
What is the Formula for Flow Meter Calibration?
The formula for flow meter calibration depends on the type of flow meter being calibrated.
For differential pressure (DP) flow meters, the formula is typically:
Q = K * (P1 - P2)^0.5
where Q is the flow rate, K is the calibration factor, P1 is the pressure upstream of the flow meter, and P2 is the pressure downstream of the flow meter.
For turbine flow meters, the formula is usually:
Q = K * N
where Q is the flow rate, K is the calibration factor, and N is the number of revolutions of the turbine.
For electromagnetic flow meters, the formula is:
Q = K * V
where Q is the flow rate, K is the calibration factor, and V is the average velocity of the fluid as it passes through the flow meter.
These are just a few examples, as different flow meter types may have different calibration formulas. It is important to consult the manufacturer's specifications and guidelines for the specific flow meter being calibrated.

Why Should the Flow Meter Be Calibrated?
Flow meters should be calibrated to ensure that they are providing accurate and reliable measurements of flow rate. Over time, various factors such as wear and tear, buildup of debris or contaminants, and changes in environmental conditions can cause the flow meter to drift from its original calibration. This can result in inaccurate measurements that may lead to errors in process control, wasted materials, or even safety hazards. Calibration helps to ensure that the flow meter is measuring flow accurately and within acceptable tolerances, and can help to identify and correct any issues before they cause larger problems.
Flow Meter Calibration vs. Recalibration
Flow meter calibration is the process of adjusting the equipment to measure flow rate with a predetermined accuracy, whereas recalibration means making adjustments to existing equipment to bring it back up to a predetermined standard. Calibration typically involves testing the flow meter to see if it is within a certain range of accuracy and then making adjustments or changes to the equipment to bring it up to a level of accuracy that is acceptable. Recalibration on the other hand, is the process of adjusting existing equipment to bring back accuracy that has been lost due to either wear and tear or other factors. The main difference between calibration and recalibration is that calibration typically requires more time and resources up front, whereas recalibration requires less time and resources.
Factors Affecting the Accuracy of Flow Meters
There are several factors that can affect the accuracy of flow meters. Some of the most common factors include:
Fluid Properties: The properties of the fluid being measured can have a significant impact on the accuracy of flow meters. For example, highly viscous or abrasive fluids can cause wear and tear on the flow meter, leading to inaccurate readings.
Flow Profile: The flow profile of the fluid being measured can also impact accuracy. Turbulent flows, for example, can cause eddies and swirls that can affect the performance of some flow meters.
Installation: The installation of the flow meter can also affect accuracy. Improper installation, such as having the meter installed too close to bends or elbows in the pipe, can cause turbulence and affect readings.
Temperature and Pressure: Changes in temperature and pressure can also affect the accuracy of flow meters. Changes in these factors can cause the fluid's viscosity to change, leading to inaccurate readings.
Calibration: As mentioned earlier, flow meter calibration is essential for maintaining accuracy. Failure to calibrate the flow meter regularly can result in inaccurate readings.
By taking these factors into consideration and regularly calibrating flow meters, it is possible to ensure accurate flow measurements.
Other factors:
- Operating range – Flow meters can be calibrated to measure a specific range of flow rate. If the range changes, the accuracy of the meter can be affected.
- Material – The type of material the flow meter is made of can affect its accuracy.
- Shape and size – The shape and size of the flow meter can impact the accuracy.
- Flow range – The flow range of the meter can affect its accuracy.
- Instruments – The type of instruments used to measure the flow rate can affect the accuracy of the meter.
- External influences – Factors such as vibrations, dust and dirt, and moisture can all have an effect on the accuracy of a flow meter.

What is the Importance of Calibrating the Flow Meter?
Calibrating a flow meter is important to ensure accuracy in the measurements taken. A calibrated flow meter is able to provide more accurate readings, which in turn can help improve precision and accuracy in operations. Additionally, a calibrated flow meter can provide more stable readings even when the flow rate fluctuates, which can help reduce costs associated with any inaccuracies in readings. Calibration can also help identify any issues with a flow meter so that they can be addressed and corrected.
How Often is Electromagnetic Flow Meter Calibration Needed?
The frequency of electromagnetic flow meter calibration should be determined based on the specific application. Generally, it is recommended that the device be calibrated at least once annually, or more frequently if the device is exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Additionally, calibration should be done more frequently if any changes have been made to the device, such as replacing parts or making adjustments.
What Could Occur If the Flow Meter is not Correctly Calibrated?
If a flow meter is not correctly calibrated, this can lead to inaccurate measurements which can in turn lead to incorrect data and assumptions. This can result in reduced efficiency and productivity, incorrect analysis of the data, and potentially even misinformed decision making. Additionally, incorrect calibration can lead to inaccurate invoice calculations, overcharging and undercharging customers, and can impact the accuracy of financial statements.
How Do You Calibrate an Electromagnetic Flow Meter?
The process for calibrating an electromagnetic flow meter typically involves connecting the meter to a controlled source that can provide a known and consistent flow rate. Once connected, the flow rate of the source is adjusted to the desired rate and the meter readings are noted. Any discrepancies between the actual flow rate and the flow rate as measured by the meter can be noted and used to adjust the meter's calibration settings accordingly. Additionally, the meter's accuracy can be checked by running several tests at different flow rates.
The methods of calibrating an Electromagnetic Flow Meter include:
- 1.Zero or Span Calibration
- 2.Starting Point Calibration
- 3.Matching to a Primary Standard Flow Meter
- 4.Fluid Prover Calibration
- 5.Pipe Prover Calibration
- 6.Reverse Flow Calibration
- 7.Correlation Calibration
- 8.Ground Calibration
- 9.Flow Range Test
- 10. Pulse Test Calibration
The Zero or Span Calibration
Zero or Span Calibration is a method of calibrating an electromagnetic flow meter which is used to verify the accuracy of the meter's zero and span points. This type of calibration is done by running water through the meter at zero flow and then at a known higher flow rate, and then comparing the meter's readings with the known values. If the readings are accurate, then the meter is considered to be calibrated.
The Starting Point Calibration
Starting Point Calibration is a method of calibrating an electromagnetic flow meter which is used to verify the accuracy of the meter's starting point (zero flow point). This type of calibration is done by running water through the meter at zero flow and comparing the meter's reading with a known value. If the readings are accurate, then the meter is considered to be calibrated.
Matching to a Primary Standard Flow Meter
Matching to a Primary Standard Flow Meter is a method of calibrating an electromagnetic flow meter which is used to verify the accuracy of the meter. This type of calibration is done by running water through the primary standard flow meter and the electromagnetic flow meter and comparing the readings of the two meters. If the readings of the two meters match, then the electromagnetic flow meter is considered to be calibrated.
Fluid Prover Calibration
Fluid Prover Calibration is a method of calibrating an electromagnetic flow meter which is used to verify the accuracy of the meter. This type of calibration is done by running water through a fluid prover and the electromagnetic flow meter and comparing the readings of the two devices. If the readings of the two devices match, then the electromagnetic flow meter is considered to be calibrated.
Pipe Prover Calibration
Pipe Prover Calibration is a method of calibrating an electromagnetic flow meter which is used to verify the accuracy of the meter. This type of calibration is done by running water through a pipe prover and the electromagnetic flow meter and comparing the readings of the two devices. If the readings of the two devices match, then the electromagnetic flow meter is considered to be calibrated.
Reverse Flow Calibration
Reverse Flow Calibration is a method of calibrating an electromagnetic flow meter which is used to verify the accuracy of the meter by running water through it in reverse direction. This type of calibration is done by running water in reverse direction through the electromagnetic flow meter and comparing the readings of the meter with a known value. If the readings are accurate, then the meter is considered to be calibrated.
Correlation Calibration
Correlation Calibration is a method of calibrating an electromagnetic flow meter which is used to verify the accuracy of the meter. This type of calibration is done by running water through two or more flow meters, such as an electromagnetic flow meter, a turbine meter and a positive displacement meter, and comparing their readings. If the readings of the flow meters correlate, then the electromagnetic flow meter is considered to be calibrated.
Ground Calibration
Ground Calibration is a method of calibrating an electromagnetic flow meter which is used to verify the accuracy of the meter. This type of calibration is done by comparing the meter's readings with a reference ground point, such as a reference pot or a reference electrode, and ensuring that the reading is accurate. If the readings are accurate, then the meter is considered to be calibrated.
Flow Range Test
Flow Range Test is a method of calibrating an electromagnetic flow meter which is used to verify the accuracy of the meter across its entire range of flow rates. This type of calibration is done by running water through the meter at various flow rates and comparing the meter's readings with a known value. If the readings are accurate, then the meter is considered to be calibrated.
Pulse Test Calibration
Pulse Test Calibration is a method of calibrating an electromagnetic flow meter which is used to verify the accuracy of the meter's pulse output signals. This type of calibration is done by running water through the meter and comparing the pulse output signals with a known value. If the output signals are accurate, then the meter is considered to be calibrated.
Sinomeasure Electromagnetic Flow Meters Solution
Sinomeasure has been producing, developing and selling electromagnetic flow meters for more than 16 years, providing accurate and reliable solutions for industrial applications such as water treatment, sewage treatment, food and beverage. Sinomeasure has been committed to meeting the highest standards of quality and reliability in all its products. The company's electromagnetic flow meters are designed to meet the needs of many different industries, offering accuracy, reliability, and performance in challenging conditions. Sinomeasure has a strong portfolio of products, including both fixed and portable electromagnetic flow meters.
The company also offers custom solutions to meet specific customer needs, all tested and approved by independent laboratories and industry experts. In addition, Sinomeasure offers a full range of support services for their customers, including installation, maintenance, calibration, and application support. Sinomeasure's commitment to providing quality products and services has earned them recognition from the industry and from their customers. With decades of experience and expertise in the field, Sinomeasure continues to strive for excellence in their products and services, ensuring reliable performance and operation. If you have any need in process automation sensors such as flow meters, pressure transmitters, level meters, etc., please feel free to contact us.

 Español
Español Русский
Русский 







