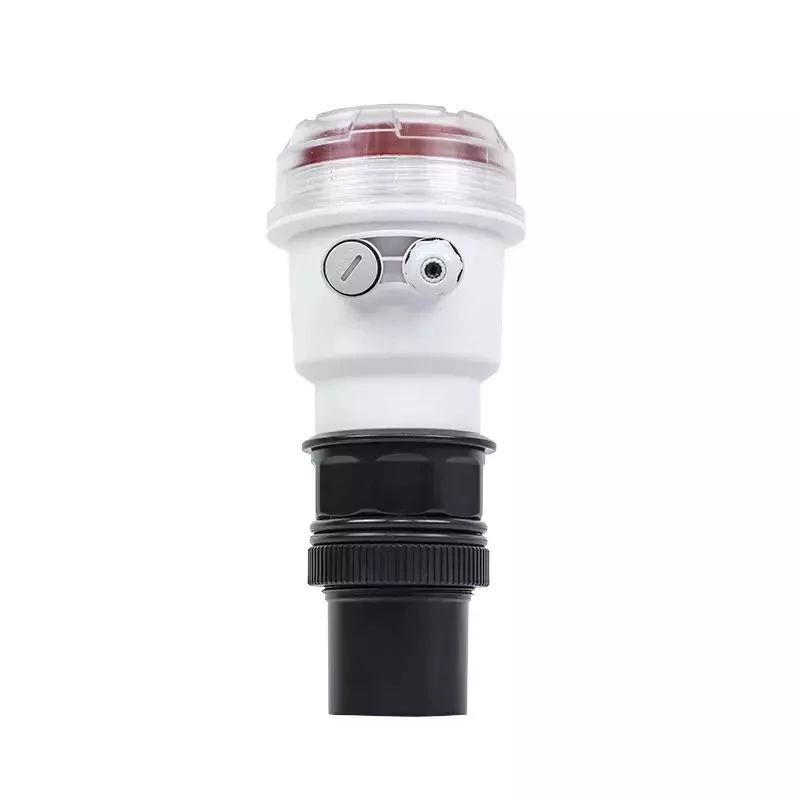
What is a flow meter for chilled water?
A flow meter for chilled water is a device that measures the volume or rate of flow of chilled water within a cooling system. It is typically installed in the piping system and can provide valuable information about the operation and efficiency of the system.
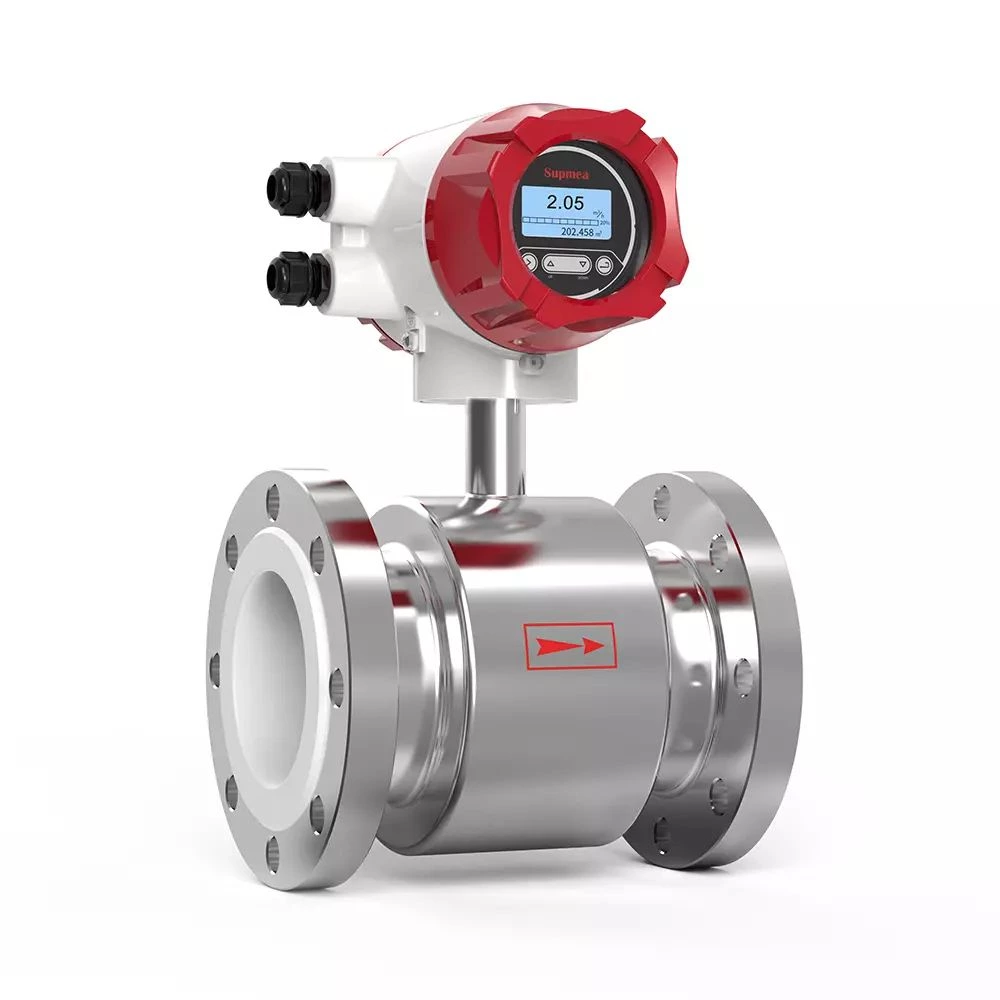
The flow meter works by utilizing various technologies such as electromagnetic, ultrasonic, vortex shedding, or thermal dispersion to detect the movement of chilled water through the pipe. It then converts the data into a readable form such as flow rate, total volume, or mass flow.
Flow meters for chilled water are commonly used in commercial and industrial applications, such as in air conditioning systems, data centers, and manufacturing processes. They help facility managers and engineers to optimize the performance of the cooling system, detect leaks, and identify potential maintenance issues. The data provided by the flow meter can also be used for billing and cost allocation purposes.
How do you measure the chilled water flow rate?
There are several ways to measure the chilled water flow rate, and the most appropriate method depends on the specific application and system requirements. Here are some of the most common methods for measuring the chilled water flow rate:
Flow Meter: The most accurate way to measure the chilled water flow rate is to install a flow meter in the piping system. As discussed earlier, there are various types of flow meters available, such as electromagnetic, ultrasonic, vortex shedding, or thermal dispersion, which can provide accurate and reliable flow rate data.
Differential Pressure Flow Measurement: This method involves measuring the pressure difference across an orifice plate, Venturi tube, or flow nozzle installed in the piping system. The flow rate can then be calculated using the measured pressure drop and the geometry of the flow restriction device.
Thermal Dispersion Flow Measurement: This method uses a thermal sensor to measure the temperature difference between two points in the piping system. As chilled water flows past the sensor, it transfers heat from one sensor to the other. The flow rate can be calculated based on the measured temperature difference and the thermal properties of the fluid.
Weighing Method: This method involves measuring the weight of chilled water passing through a container or tank over a given period of time. The flow rate can be calculated based on the measured weight and the density of the fluid.
In summary, measuring chilled water flow rate can be achieved through various methods, including installing a flow meter, using differential pressure flow measurement, thermal dispersion flow measurement, or the weighing method. The most appropriate method depends on the specific application and system requirements.
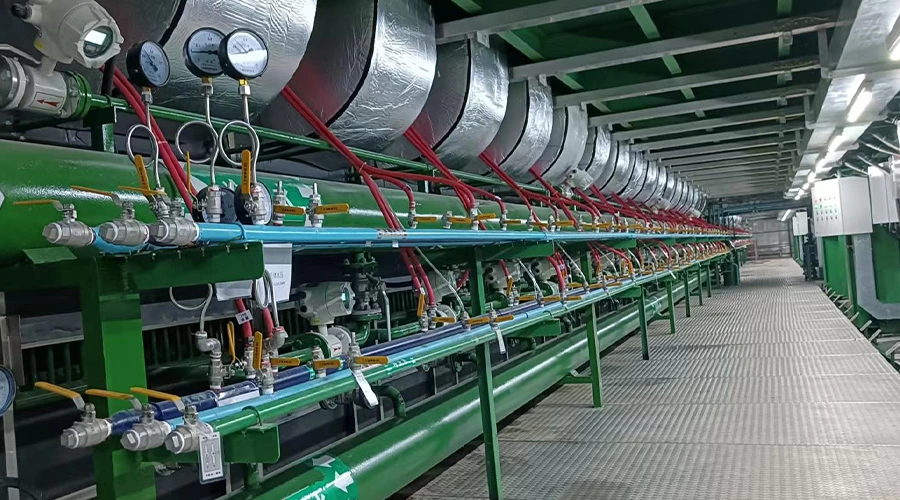

Types of chilled water flow meters
There are several types of chilled water flow meters available, each with its own unique working principle. However, most chilled water flow meters operate by detecting the movement of the chilled water through a pipe and converting that movement into a measurable signal. Here are a few examples of how some common types of chilled water flow meters work:
Electromagnetic Flow Meters: These flow meters work by passing a magnetic field through the chilled water flowing through a pipe. The magnetic field induces an electric current in the water, and the flow meter measures the voltage generated by this current. The voltage is directly proportional to the flow rate, and the flow meter can use this data to calculate the volume of chilled water flowing through the pipe.
Ultrasonic Flow Meters: Ultrasonic flow meters use sound waves to measure the velocity of chilled water flowing through a pipe. The flow meter sends ultrasonic waves through the water at an angle, and the waves are reflected back to the flow meter. The flow meter measures the time it takes for the waves to travel upstream and downstream, and uses this data to calculate the flow rate.
Vortex Shedding Flow Meters: These flow meters work by detecting the frequency at which vortices (eddies) are shed from a bluff body placed in the chilled water flow stream. The frequency of the vortices is directly proportional to the flow rate. The flow meter can use this data to calculate the volume of chilled water flowing through the pipe.
Thermal Dispersion Flow Meters: These flow meters work by measuring the temperature difference between two temperature sensors placed in the chilled water flow stream. As the chilled water flows past the sensors, it transfers heat to the sensor with a lower temperature. The flow meter measures the temperature difference between the two sensors, and uses this data to calculate the flow rate.
In summary, chilled water flow meters work by detecting the movement of chilled water through a pipe and converting that movement into a measurable signal using various technologies.
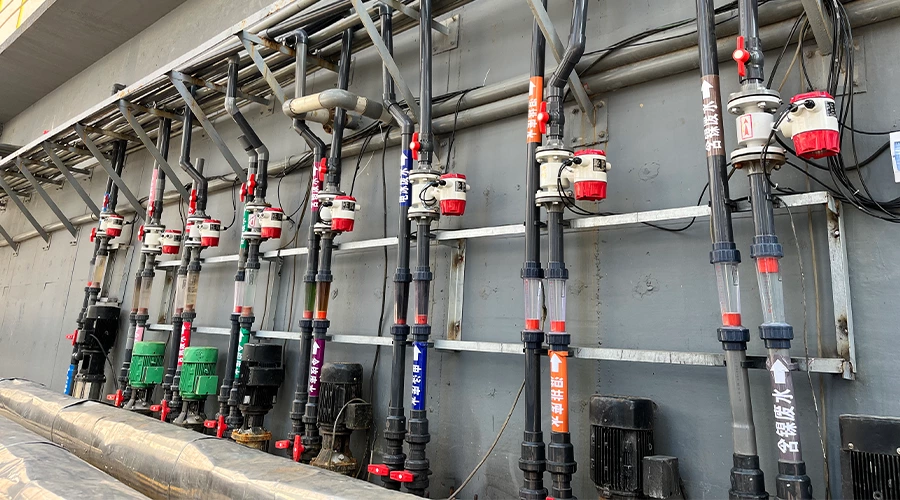

What is the chiller flow rate?
Chiller flow rate refers to the volume of chilled water that flows through a chiller unit over a given period of time. It is an important parameter to monitor and control in chiller systems as it affects the efficiency, capacity, and performance of the chiller.
The chiller flow rate is typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM) and can be calculated using the following formula:
Chiller Flow Rate = Chilled Water Load / (Chilled Water Supply Temperature - Chilled Water Return Temperature) x 500
where:
- Chilled Water Load: The amount of heat that needs to be removed from the process or building being cooled, typically measured in BTUs per hour or kilowatts.
- Chilled Water Supply Temperature: The temperature of the chilled water leaving the chiller unit.
- Chilled Water Return Temperature: The temperature of the chilled water returning to the chiller unit.
- 500: A constant that converts the units from BTUs per hour to gallons per minute.
By measuring and controlling the chiller flow rate, facility managers can ensure that the chiller operates efficiently and effectively, reducing energy costs and minimizing maintenance requirements. The flow rate can be adjusted by changing the pump speed or modifying the piping system.